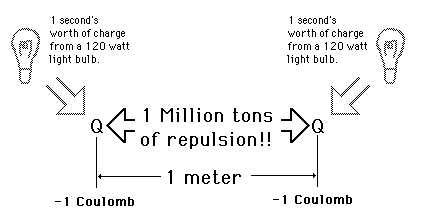
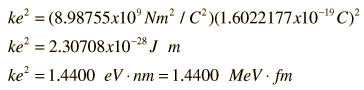Coulomb's Law
Like charges repel, unlike charges attract.
The electric force acting on a point charge 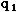 as a result of the presence of a second point charge
as a result of the presence of a second point charge 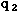 is given by Coulomb's Law:
is given by Coulomb's Law:
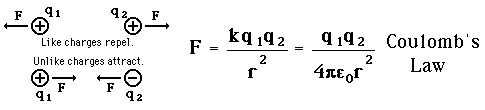
where
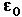 = permittivity of space
= permittivity of spaceNote that this satisfies Newton's third law because it implies that exactly the same magnitude of force acts on 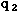 . Coulomb's law is a vector equation and includes the fact that the force acts along the line joining the charges. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. Coulomb's law describes a force of infinite range which obeys the inverse square law, and is of the same form as the gravity force.
. Coulomb's law is a vector equation and includes the fact that the force acts along the line joining the charges. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. Coulomb's law describes a force of infinite range which obeys the inverse square law, and is of the same form as the gravity force.
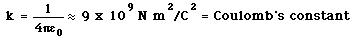
| Electric force example |
| More on Coulomb's constant |
Electromagnetic force